A circuit breaker is a vital electrical device that protects an electrical circuit from damage due to overcurrent, short circuit or electrical fault. Unlike fuses which need to be replaced after one time use, a circuit breaker can be reset manually or automatically after an interruption.
How Circuit Breakers Works
Circuit breaker works by automatically interrupting the flow of electricity when abnormal conditions such as excessive current or short circuit is detected. This interruption prevents overheating, fire and damage to electrical appliances. When the breaker detects a fault it trips the switch and cuts off power until the issue is resolved.
Types of Circuit Breakers (CB)
There are several types of circuit breakers, classified on their construction & operating principles:
1. Based on Voltage Levels
• Low-Voltage Circuit Breakers: Most Common used in homes and offices (e.g., miniature circuit breakers or MCBs).
• Medium-Voltage Circuit Breakers: Used in industrial applications.
• High-Voltage Circuit Breakers: Used in power grids & substations.
2. Based on Arc Extinguishing Medium
• Air Circuit Breakers (ACB): Uses air to extinguish the arc.
• Oil Circuit Breakers (OCB): Uses oil as an insulating medium to quench arcs.
• Vacuum Circuit Breakers (VCB): Uses vacuum to suppress the arc.
• SF6 Circuit Breakers: Uses sulfur hexafluoride gas for insulation and arc extinction.
3. Based on Mechanism
• Thermal Circuit Breakers: Trips when excessive heat is generated.
• Magnetic Circuit Breakers: Operates when high current generates a strong magnetic field.
• Hybrid Circuit Breakers: Combines both thermal and magnetic protection.
Importance of Circuit Breakers
Circuit breaker plays a crucial role in:
• Protecting Electrical Systems: Preventing overheating & electrical fires.
• Ensuring Equipment Long Life: Protecting appliances from power surges.
• Improving Safety: Provides a means to isolate faults.
• Minimizing Down time: Quick reset capability minimizes disruption.
How to Choose the Right Circuit Breaker
Choosing the right circuit breakers depends on:
• Load requirement & current rating.
• Environmental conditions (e.g, temperature, humidity).
• Types of appliances being protected.
• Compliance to electrical safety standards.
Different types of circuit breakers and their functions
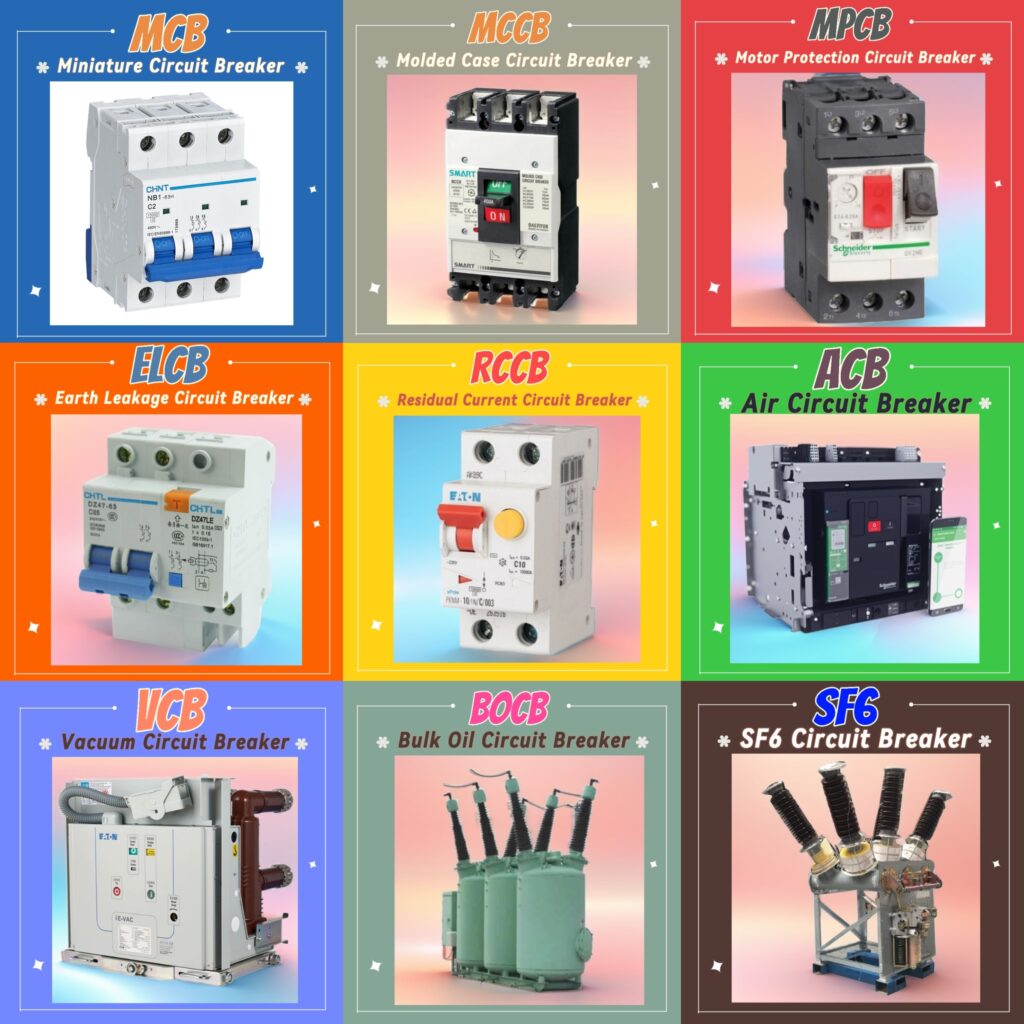

Circuit Breaker is an essential Device in electrical systems to protect circuits from overcurrent, short circuits & other electrical faults. There are various types of circuit breakers available, each designed for specific applications based on voltage levels, fault types & environmental conditions. This article will cover different types of circuit breakers, their functions & where they are used.
1-Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)

Overview:
MCB is a low voltage circuit breaker used to protect electrical circuits from overload & short circuit in residential & commercial applications.
Features:
- Trips automatically in case of overload.
- Available in single pole, double pole & multi pole.
- Rated up to 125A.
Applications:
Homes, offices & commercial buildings for lighting & appliance protection
2-Molded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB)

Overview:
MCCBs are used for higher current applications than MCBs & provides protection against overloads & short circuits.
Features:
- Adjustable trip settings for overcurrent protection.
- Up to 2,500A current handling.
- Industrial applications.
Applications:
Factories, commercial buildings & electrical distribution panels.
3- Motor Protection Circuit Breaker (MPCB)

Overview:
MPCB is used to protect electric motors from overload, phase failure & short circuits.
Features:
- Thermal / magnetic protection.
- Adjustable settings for different motor ratings.
- Protection against phase imbalance.
Applications:
Industrial motors, pumps & conveyor systems
4-Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB)

Overview:
ELCB detects leakage currents that may occur due to insulation failure or accidental contact with electrical components & provides protection against electric shocks.
Features:
- Voltage based leakage detection.
- Trips the circuit when leakage exceeds safe limits.
Applications:
Older electrical installations & residential buildings.
5-Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB)
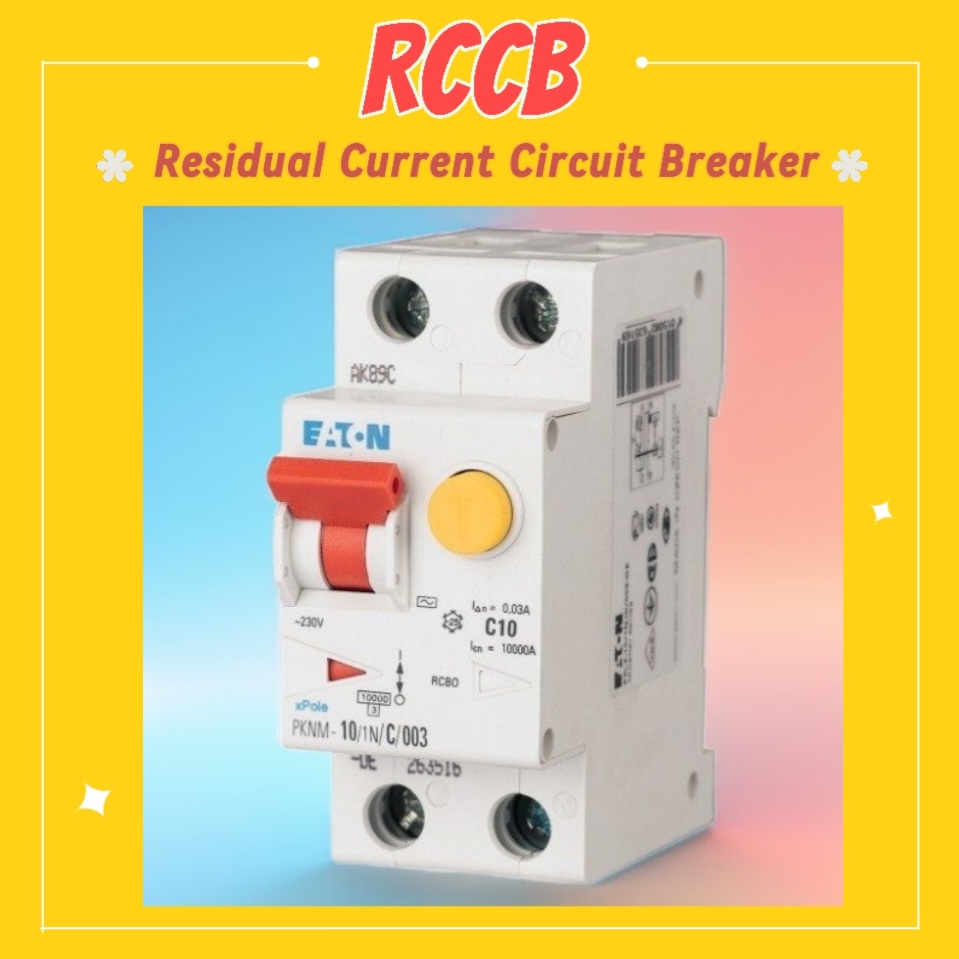
Overview:
RCCBs monitors the current flow & trips the supply if leakage is detected & provides protection against electric shock & fire hazards.
Features:
- Operates by sensing the imbalance between live & neutral currents.
- Rated at 30mA or 100mA.
Applications:
Homes, hospitals & workplaces for human safety.
6-Air Circuit Breaker (ACB)

Overview:
ACBs are used in high voltage & high current applications, air as the arc-quenching medium.
Features:
- Up to 6,300A current rating.
- Frequent switching operation.
- Adjustable trip settings for different fault levels.
Applications:
Power plants, data centers& industrial switchboards.
7-Vacuum Circuit Breaker (VCB)

Overview:
VCBs uses vacuum as the arc-quenching medium & used for medium voltage applications.
Features:
- High vacuum dielectric strength.
- Low maintenance.
- Up to 38kV voltage rating.
Applications:
Power distribution networks & substations.
8-Oil Circuit Breaker (OCB or BOCB – Bulk Oil Circuit Breaker)
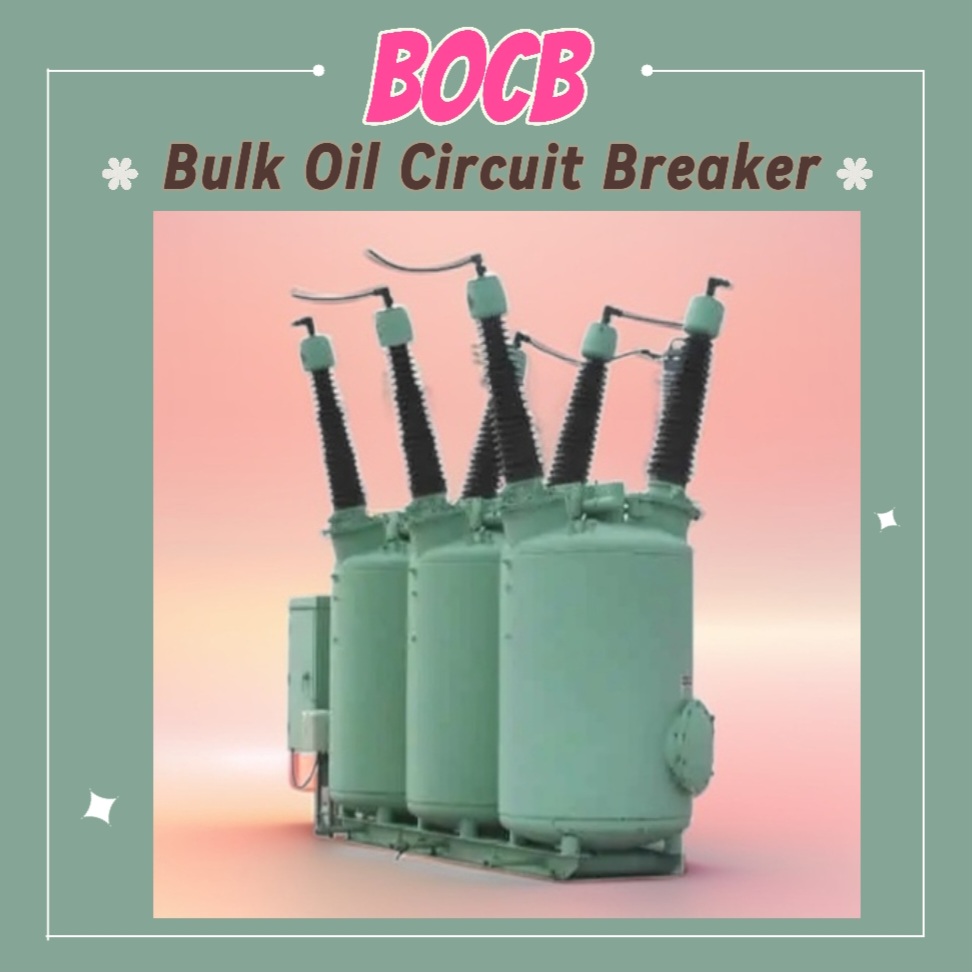
Overview:
OCBs uses insulating oil to quench the arc during fault conditions & provides reliable protection for high voltage systems.
Features:
- Good cooling & arc extinction properties.
- Oil maintenance required.
- Outdoor applications.
Applications:
Rural power distribution & substations.
9-SF6 Circuit Breaker

Overview:
SF6 (Sulfur Hexafluoride) circuit breakers use SF6 gas as an insulating & arc-quenching medium, it has excellent electrical properties.
Key Features:
- High dielectric strength & arc-extinguishing capabilities.
- Up to 800kV.
- Compact & reliable.
Applications:
High voltage substations & power transmission.
Conclusion
Circuit breakers are essential part of any electrical system. Choosing the right circuit breaker is very important to ensure the safety, reliability and efficiency of the system. Current rating, voltage level, application requirements should be considered while selecting a breaker. Knowing the difference between MCB, MCCB, MPCB, ELCB, RCCB, ACB, VCB, OCB, SF6 circuit breaker will help you to take a right decision for your electrical protection needs. Maintenance & correct installation is key to ensure they work long term.

Title: Circuit Breakers, Types & Functions
Language: English
Size: 1.6MB
Pages: 21
Format: PDF



Hello! I hope you’re having a great day. Good luck 🙂
Si te apasiona los sitios de apuestas en linea en Espana, has llegado al sitio adecuado. Aqui encontraras resenas actualizadas sobre los mejores casinos disponibles en Espana.
Beneficios de los casinos en Espana
Licencias oficiales para jugar con total confianza.
Bonos de bienvenida exclusivos que aumentan tus posibilidades de ganar.
Ruleta, blackjack, tragaperras y mas con premios atractivos.
Transacciones confiables con multiples metodos de pago, incluyendo tarjetas, PayPal y criptomonedas.
?Donde encontrar los mejores casinos?
En nuestra guia hemos recopilado las opiniones de expertos sobre los sitios mas confiables para jugar. Consulta la informacion aqui:
http://www.casinotorero.info
Empieza a jugar en un casino confiable y descubre una experiencia de juego unica.